Building Smart Cities Interconnectivity: The Role of Smart Digital Infrastructure in 2023 and Beyond!
Athena Smart City
By Dr. Daniele Gambero, PhD
The concept of a smart city has emerged as a promising solution to address the complex challenges of urbanization and improve the quality of life for residents. A smart city leverages advanced technologies, data analytics, and interconnected systems to optimize urban infrastructure, enhance efficiency, promote sustainability, and foster citizen well-being.
In an increasingly urbanized world, the concept of a “smart city” has gained significant traction as a solution to enhancing urban living. At the heart of any smart city lies a robust digital infrastructure that fosters interconnectivity among various systems and stakeholders.
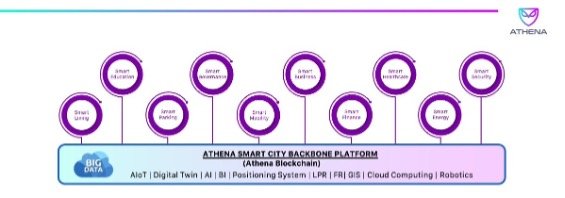
By integrating various components and stakeholders, smart cities aim to create interconnected and intelligent urban environments. Hence, in a smart city, a digital infrastructure serves as the backbone that enables seamless communication, data collection, and analysis.
This smart infrastructure encompasses a wide range of elements and components that, working together, allow to gather and process real-time data, facilitating evidence-based decision-making and efficient resource allocation. This article delves into the transformative power of smart city digital infrastructure and explores how it enables interconnectivity to revolutionize urban environments.
By examining the key components, benefits, challenges, and future prospects, we unravel the immense potential of digital infrastructure in shaping the cities of tomorrow.
Defining Smart City Digital Infrastructure
Smart city digital infrastructure refers to the underlying framework of interconnected technologies that enable the seamless flow of data and communication within a city. It encompasses a wide range of components, including sensor networks, data centres, communication networks, cloud computing, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
These elements work in unison to collect, process, analyse, and disseminate data, empowering city administrators, businesses, and residents with valuable insights and real-time information.
Key Components of Smart City Digital Infrastructure
a) Sensor Networks
Sensors placed strategically throughout the city collecting data on a wide range of parameters such as air quality, traffic congestion, waste management, energy usage, and more. These sensors form the backbone of data collection in a smart city.
b) Communication Networks
High-speed, reliable communication networks, such as 5G, enable the efficient transmission of data between different devices, systems, and stakeholders. They provide the connectivity required for real-time monitoring, analysis, and response.
c) Data Centres
Data centres store and process the vast amounts of data generated by the smart city infrastructure. They employ advanced technologies like cloud computing and edge computing to handle data efficiently providing easily scalable data storage.
d) Internet of Things (IoT) Devices
IoT devices, embedded with sensors and connectivity, facilitate the interconnection of physical objects, enabling real-time data collection and analysis. These devices can include smart streetlights, waste management systems, parking sensors, storm water monitoring systems and more.
e) Cloud Computing
Cloud-based platforms allow for the storage, processing, and analysis of large datasets. They provide easy scalability, secure accessibility, and cost- effectiveness to handle the exponential growth of data in smart cities.
What are the Benefits of Interconnectivity in Smart Cities
a) Improved Efficiency
Interconnectivity enables the optimization of urban services, such as transportation, energy distribution, waste management, and public safety. Real-time data collection and analysis allow for efficient resource allocation, reducing congestion, energy over consumption, and operational costs.
b) Enhanced Quality of Life
Interconnectivity fosters a better quality of life for all residents. It enables real-time monitoring of air quality, noise levels, and traffic conditions, leading to quicker response times and improved citizen safety. Smart city infrastructure also supports amenities like smart grids, intelligent transportation systems, and smart homes, enhancing convenience and comfort for residents.
c) Economic Growth
Smart city initiatives, when property planned and executed, will attract businesses and investment, fuelling economic growth to a totally new level. Interconnectivity supports innovation and entrepreneurship, creating new job opportunities in sectors such as technology, data analytics, and a wide range of urban services.
d) Citizen-centric
A Smart Digital Infrastructure empowers citizens by providing access to real-time information, enabling them to actively participate in decision-making processes. Through mobile apps and online platforms, residents can report issues, access services, and provide feedback, fostering a strong sense of community and shared responsibility.
A Smart Digital Infrastructure empowers citizens by providing access to real-time information, enabling them to actively participate in decision-making processes. Through mobile apps and online platforms, residents can report issues, access services, and provide feedback, fostering a strong sense of community and shared responsibility.
Challenges and Final Considerations
The vast amount of data collected in smart cities has raised serious concerns about privacy and security. Protecting personal information and ensuring data protection and security are paramount to building trust among citizens and stakeholders.
Unequal access to digital technologies can widen the divide within cities, leaving certain communities, the more fragile from an education and income stand point, excluded from the actual benefits of smart city infrastructure. Efforts must be made by all stakeholders to bridge this divide and ensure the highest possible inclusivity.
As urban centres sprawl and technology advances, scalability and integration have become the key challenges. Smart city digital infrastructure needs to ensure high flexibility and adaptability to accommodate evolving needs of all citizens and seamlessly integrate with existing systems.
Developing and maintaining smart city infrastructure requires strong and transparent collaboration among many stakeholders, including government agencies, private companies, and citizens. Effective partnerships, coordination, trust and transparency building are crucial to ensure the success and sustainability of smart city initiatives.
Future Prospects and Conclusion
As technology continues to evolve at increasing pace, the potential of smart city digital infrastructure will keep expanding beyond what we can imagine. Advancements in artificial intelligence, edge computing, and blockchain are expected to further revolutionize urban environments.
These technologies will enhance the capabilities of smart city infrastructure, leading to more efficient resource management, improved citizen services, and increased sustainability providing their application will happen in a highly responsible manner.
In conclusion, smart city digital infrastructure plays a pivotal role in creating interconnectivity and transforming urban environments. By leveraging sensor networks, communication networks, data centres, IoT devices, and cloud computing, cities all around the world will be able to unlock countless benefits, including improved efficiency, sustainability, quality of life, economic growth, reduced inequalities, responsible use of all available resources and citizen engagement.
However, addressing challenges related to privacy, digital divide, scalability, and stakeholder collaboration is of the highest importance for the successful implementation of smart city initiatives. With continued innovation and collaboration, smart city digital infrastructure holds the promise of creating truly interconnected, efficient, and sustainable cities for the future.
Athena Smart Cities visionary founders have envisaged the urgent need of a smart, easily adaptable, hyper secured digital infrastructure and aim to offer it to as many as possible urban centres, globally! Someone has said that digital transformation needs to keep into consideration cultural and traditions driven habits; we couldn’t agree more at front end level with a commonly shared backend equal for all.
We are proudly offering a “Global Digital Platform for Local Solutions”!
Dr. Daniele Gambero is the Chief Business Development Officer for Athena Smart Cities and the current President of Malaysia Proptech Association